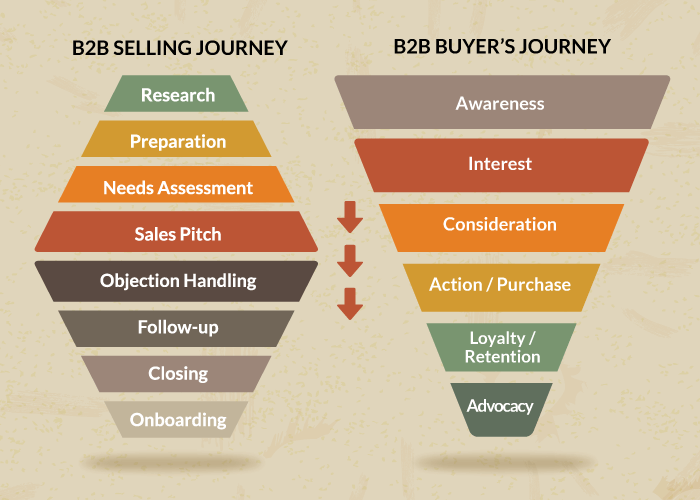
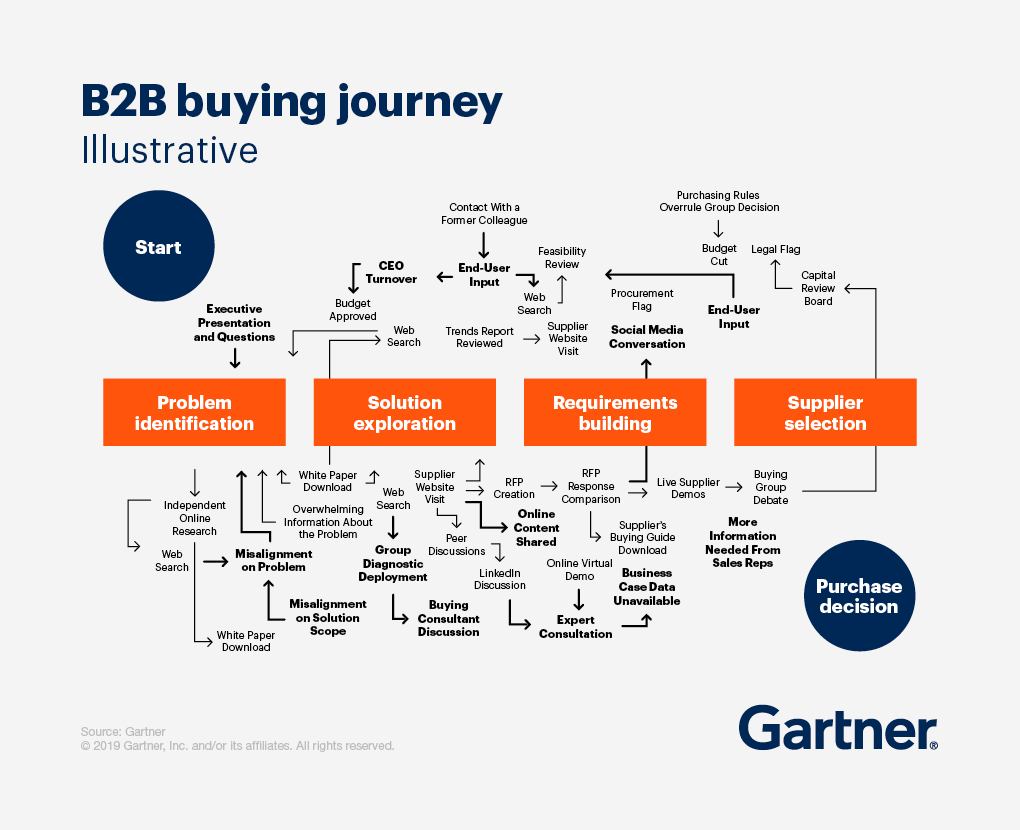
Inside sales have become the most popular sales model for B2B SaaS and many other high-ticket industries. But what are inside sales, how do they compare to outside sales, and what will the role look like in 2025?
A global health crisis forced millions of people to work from home, and many sales organizations still operate remotely. During this time, new technology also changed inside sales forever.
So, what is inside sales exactly and how is it evolving?
- Inside Sales vs Outside Sales
- Benefits of Inside Sales
- Current State of Inside Sales
- Key Skills and Responsibilities
- The Future of Inside Sales
The Meaning of Inside Sales
Inside sales are the exchange of products and services online. It is also known as “virtual sales,” “digital selling,” and “remote sales.” Inside salespeople build sales pipelines through digital channels instead of outside channels.
These are the most 5 common examples of virtual sales channels in 2025:
- Video
- Chat
- Phone
- Social media
The Difference Between Inside and Outside Sales
The main differences between inside and outside sales are travel and the workplace. Unlike outside sales, inside salespeople do not travel to visit clients off-site.
Inside sales are done in an office or remotely, on the computer, and over the phone. On the other hand, outside salespeople meet clients at off-site premises and industry events, usually for entertainment and training purposes.
Inside and outside sales can be combined for greater effectiveness. An example of this is a company that leverages remote sales for leads and account management with an outside sales team that closes bigger deals and conducts in-person training. Also, the two are often paired to upsell and cross-sell solutions.
In past years, inside sales have been considered a backup to outside sales. However, changes in B2B buying preferences have increased the importance of virtual sales in B2B SaaS.

7 Advantages of Inside Sales
The inside sales model has many advantages versus outside sales or telemarketing:
1. Scalability
Remote sales teams can quickly scale and deploy new agents in the cloud. For most businesses, their stack of sales tools is cloud-based and does not require extensive implementation.
2. Cost-effectiveness
These days, sales tech is relatively inexpensive. You can equip reps with a full stack of tools for about $200 per rep monthly.
Also, there are no relocation costs for inside sales, as you can hire talent globally to work from home. Outside sales reps carry much higher operating expenses and must travel frequently.
The salary for remote sales reps is also affordable for most companies with positive cash flow.
3. Coaching
Digital sales tools have made it easier to coach inside sales reps.
Certain talk tracks and sales methods tend to win out. As an inside sales manager, you should be fully aware of your team’s playbook and monitor how the team interacts with potential customers. This is not easily achievable when managing a field salesforce.
Conveniently, inside sales are mostly done digitally. Managers in 2025 have more tools and coaching opportunities. This is a result of better collaboration tools, cloud-based CRM, conversation intelligence, recordings, chat transcripts, and virtual writing assistants.
4. Predictable revenue
Companies can predictably forecast and measure the ROI of an inside salesperson.
This is because inside sales reps should have targeted amounts of work to achieve each week. This can include the number of chats and calls answered, outbound dials, sent emails, meetings booked, sales demos, deals won, etc. The work is closely tied to lead generation and in turn, a predictable pipeline, of which the value can be calculated.
5. Global expansion
Whether you want to expand your business to new markets or tap into a diverse talent pool, remote sales offer great potential for global expansion. It can be done virtually from anywhere in the world.
Because inside sales can be done remotely, companies can easily onboard new reps from other countries. Hiring companies only need to ensure that reps have the right equipment and credentials to use the necessary tools. A global marketplace for hiring can give your business access to better talent at competitive rates.
Inside sales also offer an opportunity to sell your products and services to customers in other countries. The work does not need to be done on-site, which enables inside sales reps to sell to customers anywhere in the world. Companies can even take advantage of international virtual numbers to simulate a local calling presence in the country of their choosing.
6. Fordism
Sales processes can be broken down and assigned to specialized roles. A traditional inside sales process might involve the following:
- Identify target companies that fit your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) or new clients that fit expansion criteria.
- Identify decision-makers at those target companies. Research potential pain points and service use cases.
- Reach out to decision-makers to understand their pain points. Try to spark an interest in your company and how your solutions could be beneficial.
- Demo the effectiveness of your products and services. Work to close the sale.
- Ensure successful onboarding of new customers. Pursue expansion opportunities.
This type of sales method is kind of like an assembly line. An inside sales manager could assign agents or reps to specialize in each task. The inside sales reps become more effective by devoting their full attention to perfecting and performing a single task.
7. Comfort
The buyer’s journey in B2B is rapidly changing. Modern buyers prefer live screen-shares and phone calls to in-person demonstrations and face-to-face meetings.
Corporate travel in 2020 also became a lot harder. Starting in 2025, requests for health documents and travel quarantines could become more common. This makes it more difficult for outside sales reps to visit clients on-site, especially in other countries. In addition, many companies are still working from home.
Interested prospects prefer to buy and sell mostly online, and savvy buyers will do more individual research before making a decision. As a result, sales organizations must remain flexible and meet buyers in their preferred mediums.
You can run inside sales from anywhere, which will make it the preferred sales model in 2025.
What Does Inside Sales Look Like in 2025?
Business changed dramatically during 2020. The whole world was quarantined for many months. This forced all executives to do more business online and over the phone, permanently changing how business is done around the world.
Keys to Running a Smooth IS Organization
There are several components that are required to run a successful inside sales organization:
- Software
Equip managers with the right tools: CRM, call recordings, conversation intelligence, etc. Similarly, inside sales agents should have the right tools; high-speed data, sales automation tools, calling service with web dialer, writing assistants, external data, etc.
- Specialization with well-defined roles
Inside sales reps are more effective when assigned to specialized roles. For example, your team should have specialized reps who identify target companies and decision-makers, other reps who reach out to those decision-makers to spark an interest, and closers who can properly communicate the value of your services and win deals.
- Sales & marketing alignment
Marketing and inside sales should be in close contact. It is the job of marketing to create brand awareness and interest and also to supply inside sales reps with the proper enablement resources to do their jobs effectively. This is when SaaS marketing agencies and general marketing firms come in handy, as their expertise can be instrumental in creating effective strategies for brand awareness and interest. Ideally, prospects should know about your business before salespeople reach out.
- Sales process
The process is key for an digital selling organization looking to scale. Ideally, managers should implement repeatable processes and properly educate their inside sales reps. This makes it easier to expand the team and in turn, grow revenue.
- Morale & a good product
In order for salespeople to do a good job, they must believe in what they’re selling and understand its value. No righteous salesperson wants to deceive buyers and sell crappy products. They should be confident in the services that they’re selling.
Day in the Life: Inside Selling Techniques
A typical day in the life of an inside salesperson involves various tasks and responsibilities, with most days spent fielding inquiries, following up with leads or clients, prospecting online, and doing admin work. Depending on the company, the job of an inside salesperson might carry over after-hours. Results come from the work that salespeople put in.
5 Skills of a High-Performing Inside Salesperson
There’s a misconception that salespeople need to be smooth talkers in order to succeed. While being articulate in conversation helps, there are more elements of a successful salesperson.
In fact, many sales leaders believe that active listening is the number one digital selling skill. These are other valuable skills:
- Active listening
- Genuine curiosity
- Consultative approach
- Rapport building
- Strong network
What Business Is Most Likely to Benefit from Inside Sales?
Does your business need remote sales? Well, it depends on where your company is in its lifecycle. It also depends on the sales cycle complexity and contract values.
Scaleups, startups, and SaaS companies are most likely to benefit from having an inside sales team. Many startups have used inside sales to hustle their way to $10 million or more ARR. Many companies will also invest in a digital selling team during their growth stages.
Future of Inside Sales: Will it Be Different in 2025?
We saw how work shifted from in-office and in-person to fully remote during the pandemic. Video conferencing exploded. Demos and screen sharing also took off. The digital funnel and virtual selling pretty much replaced in-person lunches and dinners. We don’t see many more changes occurring in the near future.
The Bottom Line: Compared to this year, inside sales processes in 2025 will not be much different. Most changes to remote sales already happened in 2020 and are here to stay.